Click here to view image
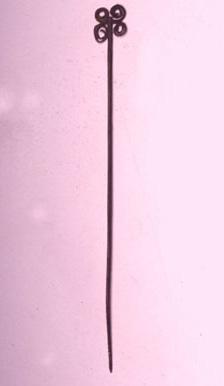
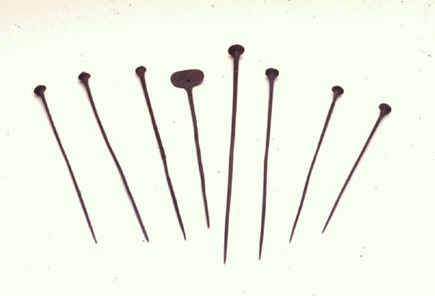
Cloak brooches
Collezione Missioni Cattoliche Americane 1893 donazione
ambito America meridionale
Cloak brooches
cloak brooches
XIX - 1893 - 1893
Unità di misura: cm; Diametro: 1; Lunghezza: 13; Varie: Diametro massimo cm 1.2; lunghezza massima cm 20.; Unità di misura: cm; Larghezza: 2.5; Diametro: 0.3; Lunghezza: 15.4; Unità di misura: cm; Diametro: 0.9; Lunghezza: 16.7; Unità di misura: cm; Diametro: 1; Lunghezza: 17.7; Unità di misura: cm; Diametro: 1; Lunghezza: 15; Unità di misura: cm; Diametro: 1; Lunghezza: 16.5; Unità di misura: cm; Diametro: 0.9; Lunghezza: 15; Unità di misura: cm; Unità di misura: cm; Unità di misura: cm
Perù
bronzo
Mostra d'arte precolombiana e di etnologia americana - Genova, Castello D'Albertis - 1972-1977
Brooches of various lengths, seven of which with a conical head and one (C.A.1695/1) with a head made up of a thin rectangular plate with rounded corners. They were originally used to stop cloaks.